Google Photos Integrates Nano Banana AI: Unlocking Gemini-Powered Image Editing and Search
Google has recently announced a major update to Google Photos, integrating its powerful AI image generation model, Nano Banana (technically known as Gemini 2.5 Flash Image), directly into the application. Debuted earlier this year, Nano Banana has quickly become renowned for its capabilities in sophisticated image manipulation, including modifying backgrounds and refining subject elements. This integration introduces a new "ask" feature, allowing users to leverage natural-language text commands to create, edit, and search their photo libraries with unprecedented ease.
The rollout commenced immediately for Android users. For iPhone users, the feature is being deployed incrementally, requiring users to ensure that the Gemini integration is enabled within their Google Photos application to access the new functionalities.

Innovative Editing and Creation Capabilities
The power of Nano Banana lies in its accessibility and deep integration with the user’s personal photo library, allowing for a level of personalized editing previously unavailable.
Natural-Language Editing with Named Subjects
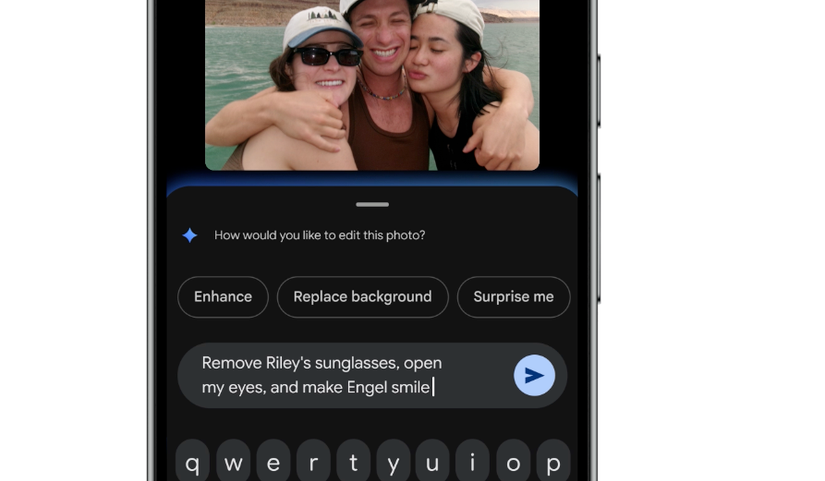
Unlike the web version of Google Gemini, which does not retain context about uploaded subjects, the Google Photos integration leverages the application's ability to recognize and name individuals in your private albums. This unlocks hyper-specific editing commands:
- If a friend named "Evan" is wearing a hat in a photo, the command "Remove Evan's hat" will prompt Nano Banana to generate a revised image where the hat is intelligently replaced based on other known photos of Evan.
- Simple edits like "remove glasses" or "change background to a tropical beach" are executed with high fidelity, demonstrating the potential of contextual AI.
Descriptive Editing Available on iOS
The introduction of this feature on the new Google Photos app for iOS provides a significant functional advantage over Apple's native Photos app, which lacks similar natural language processing for editing. iOS users will soon gain access to features like Reimagine and Autoreframe, previously exclusive to Android, enabling them to describe complex aesthetic changes that the AI executes instantly.
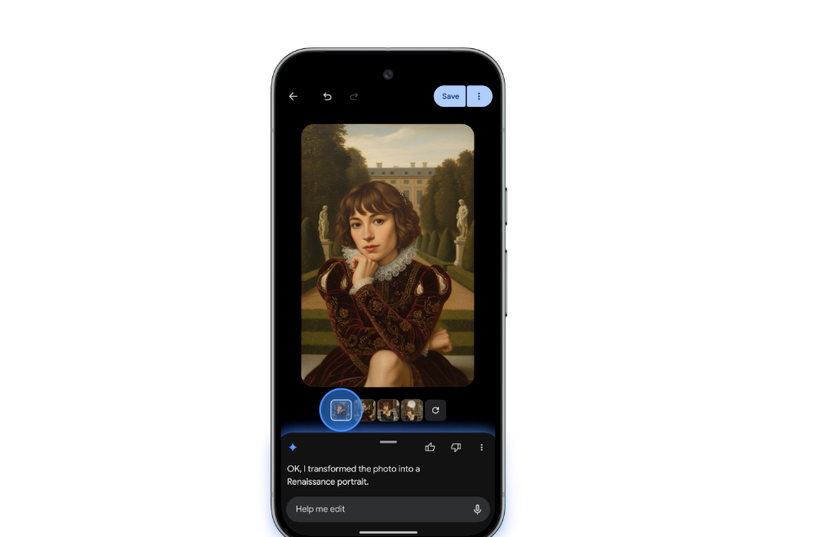
Aesthetic Style Transformation
Users can leverage text prompts to alter an image's entire aesthetic style. For example, a selfie can be instantly converted into a Renaissance-style portrait or a modern action figure graphic. While this potential is vast, users must remain aware of the inherent flaws in AI-generated imagery, such as:
- Unsettling alterations to familiar faces.
- Unreadable or garbled background text.
- Subtle, easily detectable aesthetic inconsistencies ("AI slop").
The Future of Photo Search: Ask Photos and Contextual Queries
For users with extensive photo libraries, the most impactful new feature may be the application of Gemini's powerful conversational search capabilities directly to their archives.
Ask Photos: Semantic Search and Contextual Recall
The Ask Photos feature allows users to search their images using the same natural language descriptions they would use with Google Gemini. Instead of relying solely on exact tags or metadata, search becomes semantic and contextual:
- A search for "Eiffel Tower" returns photos from a trip to Paris.
- A search for "steak" could potentially retrieve a photo of a restaurant meal, providing the user with a visual clue about the location or date of a memory.
Enhanced Contextual Learning and Q&A
A highly attractive feature for parents, students, or curious individuals is the ability to query the contents of a photograph. For instance, while reviewing a zoo trip photo, a user can input the command, "Tell me more about that bear cub." Google Photos, powered by Gemini, can then analyze the visual data and provide factual, educational information about the subject within the image.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between Nano Banana and Gemini 2.5 Flash Image?
"Nano Banana" is the internal codename for the image generation model technology that powers features like Image Flash. Google officially refers to the underlying multimodal model as Gemini 2.5 Flash Image, which is specialized for fast and high-fidelity image editing and creation tasks.
Is the Nano Banana feature available to all Google Photos users immediately?
No. The feature is immediately available to Android users. For iOS (iPhone) users, Google is rolling out the updated Google Photos app incrementally, meaning availability may vary depending on the user's region and update status.
What are the common visual flaws to look out for in AI-edited images?
Common artifacts include inaccurate or unsettling facial features on altered subjects, text in the background that appears distorted or unreadable, and general visual inconsistencies that make the image look unnaturally "smeared" or computer-generated (often referred to as AI slop).


Posting Komentar untuk "Google Photos Integrates Nano Banana AI: Unlocking Gemini-Powered Image Editing and Search"